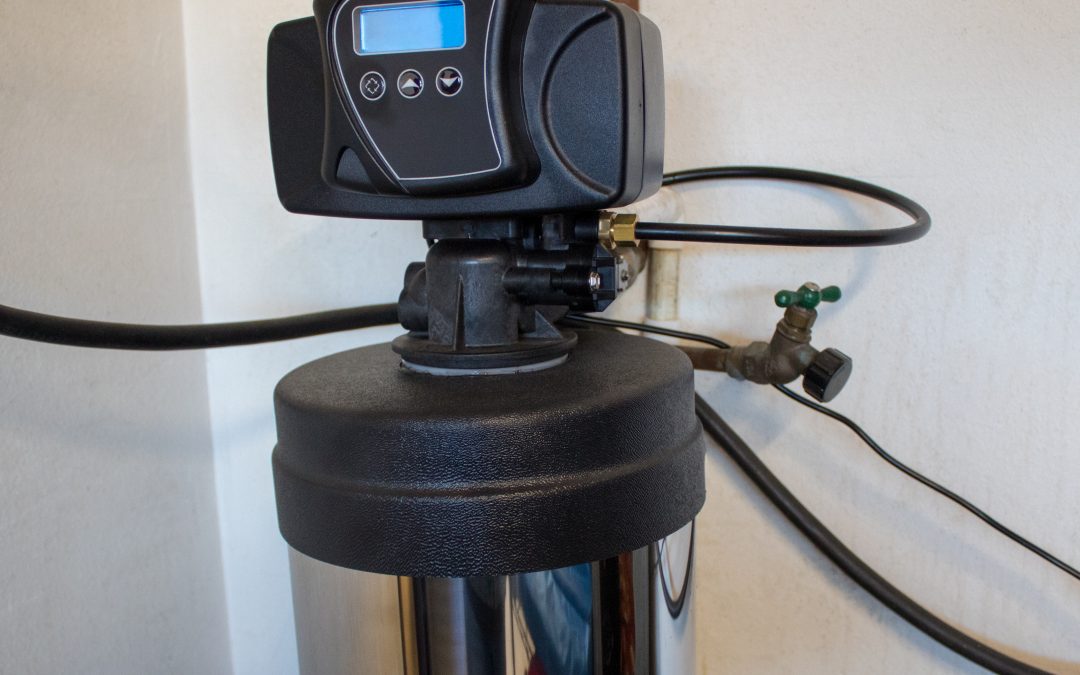
Water softeners consist of three components: a control valve, a mineral tank, and a brine tank. By removing minerals from hard water, monitoring the flow of water, and periodically cleaning the system, these three functions work together.
Mineral tank
Softening hard water takes place in the mineral tank. Water from the water supply line is fed into the tank. Calcium and magnesium ions in Best water softener are deposited on the resin beads as the water seeps through them. Flowing through your pipes and out to your household appliances, softened water leaves the tank.
Control valve
Control valves measure the amount of water flowing through the mineral tank and into your home. Water entering the mineral tank is tracked by a meter in the valve. The resin beads exchange sodium ions for hardness ions as hard water passes through the mineral tank. This reduces the resin’s capacity to continue to soften water over time.
Brine tank
Regeneration of the water softening system is assisted by the brine tank. The brine tank is short and lies adjacent to the mineral tank find more. The brine tank holds a highly concentrated solution of salt (or potassium, sometimes) that restores the resin beads’ positive charge. In the brine tank, salt is manually added as pellets or blocks. The salt dissolves in the water at the bottom of the tank. When the control valve detects that the resin’s softening capacity is diminishing, the heavy brine solution is drawn out of the tank and flushed through the resin in the mineral tank. A brine tank that runs out of salt will not soften water passing through the unit.